class
값, 상태 -> 멤버변수
Process(연산, 조건, 반복) -> method(메소드)
입출력과 Thread는 항상 예외가 발생 할 수 있다
그래서 항상 TryCatch문으로 처리를 해주어야한다
Thread는 멀티스레딩을 통해 동시에 여러 작업을 수행할 수 있도록 지원하는 클래스이다
멀티스레딩을 사용하면 CPU 자원을 더 효율적으로 활용하고 응답성을 개선할 수 있다
package p09_Thread;
public class Ex01Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 10; i >0 ; i--) {
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
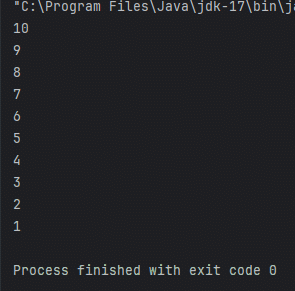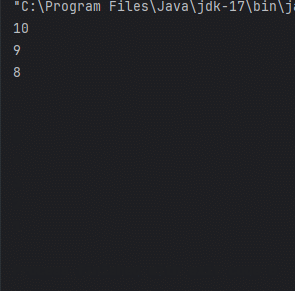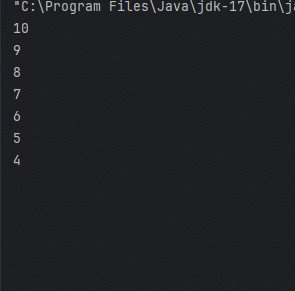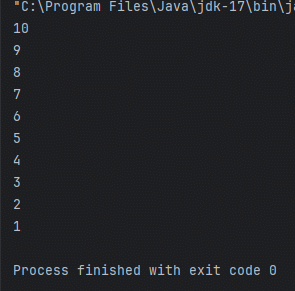
Thread의 장점으로 별도의 흐름을 생성 가능하고
자원을 절약 할 수있다
Thread 를 생성하는 방법
1)Thread를 상속
2) Runnable을 implement
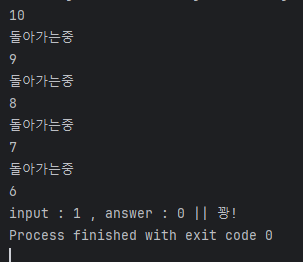
package p09_Thread;
public class Ex01Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int input = Integer.parseInt(JOptionPane.showInputDialog("빨간선(0), 파란선(1) 중에 선택하세요!"));
for (int i = 10; i >0 ; i--) {
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (input == answer) {
System.out.printf("input : %d , answer : %d || 살았다!", input, answer);
} else {
System.out.printf("input : %d , answer : %d || 꽝!", input, answer);
}
}
}
Thread를 사용하지 않고
import javax.swing.*;
import java.util.Random;
public class Ex01Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bomb bomb = new Bomb();
//Thread를 상속 받으면 그 자체로 start()를 적용할 수 잇다
//bomb.start(); //Thread 동작 시작!
//Runnalbe 을 implement 하면 Thread() 생성자 안에
//매개변수로 전달해야만 생성 가능
new Thread(bomb).start();
int input = Integer.parseInt(JOptionPane.showInputDialog("빨간선(0), 파란선(1) 중에 선택하세요!"));
bomb.choice(input);;
}
}class Bomb extends Thread {
int answer = (int) (Math.random() * 2);
boolean state_b = false;
//run : Thread의 동작을 할 때 정의한 메서드
@Override
public void run() {
state_b = true;
for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) {
if (state_b) {
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
if(!state_b) break;
System.out.println("돌아가는중");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
void choice(int input) {
if (input == answer) {
System.out.printf("input : %d , answer : %d || 살았다!", input, answer);
} else {
System.out.printf("input : %d , answer : %d || 꽝!", input, answer);
}
state_b = false;
}
}
이러한 스레드를 사용하려면
여러 스레드가 공유 자원에 접근할 때 동기화 과정에서 문제가 발생 할 수있다
' synchronized '키워드를 사용하여 데이터의 일관성을 유지하게 만든다
데이터 동기화(Synchronized)
Java에서 동기화를 위해 사용되는 키워드로, 멀티스레딩 환경에서
여러 스레드가 공유 자원에 동시에 접근할 때 발생할 수 있는 문제를 방지합니다.
synchronized 키워드를 사용하여 한 번에 하나의 스레드만
특정 블록 또는 메서드에 접근할 수 있도록 합니다.
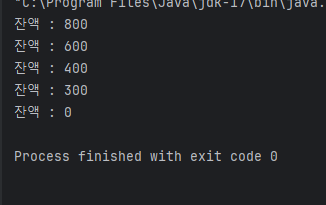
아래의 코드는 사용자의 balance 라는 주어진 값에서
100~300이라는 랜덤한 숫자를 주어
숫자만큼 값을 빼는 코드이다
package p09_Thread;
public class Ex07Synchronized {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
new Thread(customer).start();
}
}
class Account {
int balance = 1000;
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
balance -= money;
}
}
}
class Customer implements Runnable {
Account acc = new Account();
@Override
public void run() {
while (acc.getBalance() > 0) {
int money = (int) (Math.random() * 3 + 1) * 100;
acc.withdraw(money);
System.out.println("잔액 : " + acc.getBalance());
}
}
}
Thread()를 사용해서 동시성 및 병렬 처리를 하게 되면
다음과 같은 문제가 발생한다
package p09_Thread;
public class Ex07Synchronized {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
//인터페이스는 재정의한 메서드만 가져와서 사용할 수 있다
//즉, customer 안에이있는 run() 만 사용함
new Thread(customer).start();
new Thread(customer).start();
}
}
class Account {
int balance = 1000;
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
balance -= money;
}
}
}
class Customer implements Runnable {
Account acc = new Account();
@Override
public void run() {
while (acc.getBalance() > 0) {
int money = (int) (Math.random() * 3 + 1) * 100;
acc.withdraw(money);
System.out.println("잔액 : " + acc.getBalance());
}
}
}
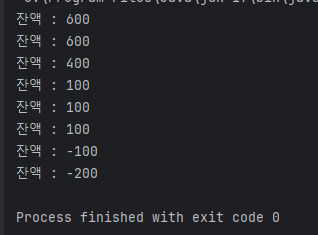
동시에 값을 들고오면서 처리를 하여
0 보다 작은 값이 나오는 경우가 발생한다
synchronized public void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
balance -= money;
}
}값을 처리하는 구간인 withdraw 에 synchronized 를 작성해
공유 자원에 동시에 접근할 때 발생할 수 있는 문제를 해결해준다
package p09_Thread;
public class Ex07Synchronized {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
//인터페이스는 재정의한 메서드만 가져와서 사용할 수 있다
//즉, customer 안에이있는 run() 만 사용함
new Thread(customer).start();
new Thread(customer).start();
}
}
class Account {
int balance = 1000;
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
synchronized public void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
balance -= money;
}
}
}
class Customer implements Runnable {
Account acc = new Account();
@Override
public void run() {
while (acc.getBalance() > 0) {
int money = (int) (Math.random() * 3 + 1) * 100;
acc.withdraw(money);
System.out.println("잔액 : " + acc.getBalance());
}
}
}
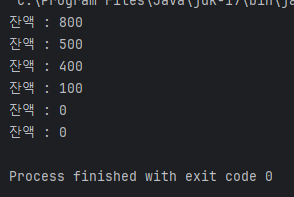
synchronized 키워드는 멀티스레드 환경에서 안전하게 자원을 공유하기 위해 사용된다


